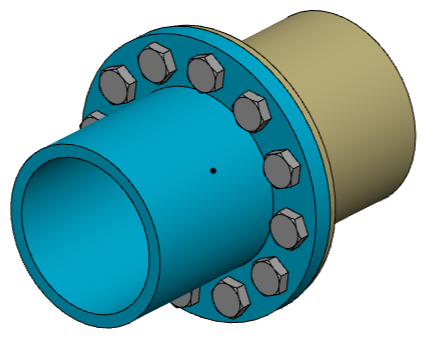
# Circular Component Pattern
Circular array can realize that an instance is based on a straight line or a reference line as the rotation axis, and a limited number of instances are copied at the uniform rotation of the axis according to the set angle. Its command interface is shown in the figure below.
Circular array is to perform arrays in two directions for the top-most instance. If a sub-instance is selected in the viewport, the array is still performed on the top-most instance where it is located. The description of each control is as follows:
Component: Pick the instance that needs to be arrayed.
Axis: Pick the axis of the array, it can be a solid edge, a reference line, or two vertices, and the array model is rotated around this axis.
Angle: Set the rotation angle of the circular array at this angle, which can be used with equal spacing.
Reverse: Set the direction of the array, and switch between the forward and reverse directions by clicking.
Number of instances: the number of entities arrayed in the current direction.
Equal Spacing: When this option is selected, the rotation angle is divided equally according to the number of instances as the included angle of adjacent instances. When this option is not selected, the set angle is used as the angle between adjacent instances.
Symmetry on both sides: When this option is selected, the array will be done in both clockwise and counterclockwise directions.
Direction 2: When this option is selected, the pattern is also performed in the opposite direction of the selected direction .
Skip instance: When checked, select the model to be skipped in the array preview, and the model will not be generated.
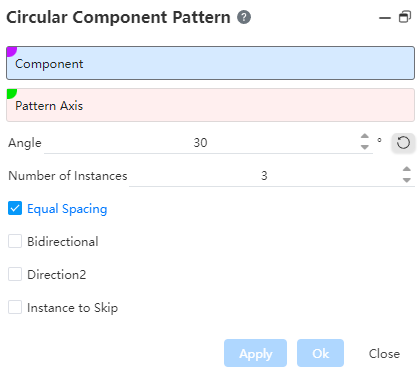
Example: Pick an instance, pick an edge as the array axis, after setting the parameters, as shown in the following figure, the example is a preview of the effect in one direction.
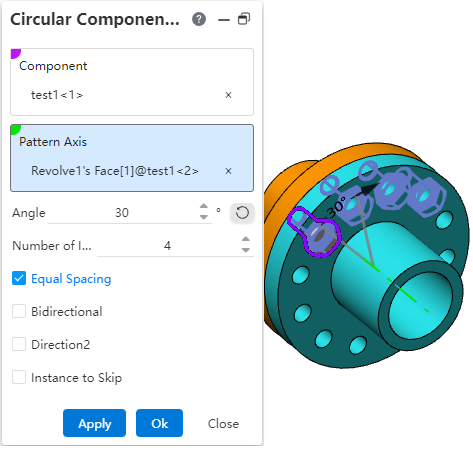
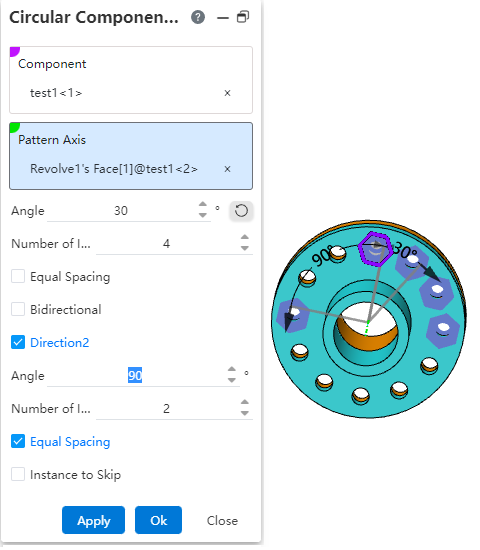
Direction 2: When there are other needs, you can check the direction 2 option, or skip the instance option, and the interface changes to the content shown in the following figure.
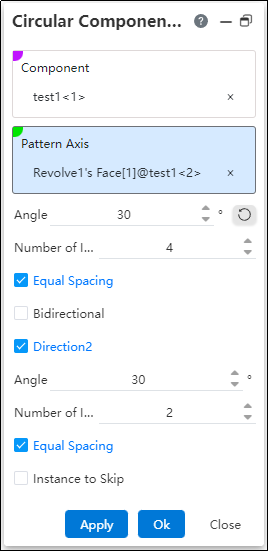
Angle: Sets the rotation angle of the ring array at this angle, which can be used with equal spacing.
Number of instances: The number of instances in the array in the current direction.
Equal Spacing: When this option is selected, the rotation angle is divided equally according to the number of instances as the included angle of adjacent instances. When this option is not selected, the set angle is used as the angle between adjacent instances.
Example: Set parameters, the preview effect is shown in the following figure:
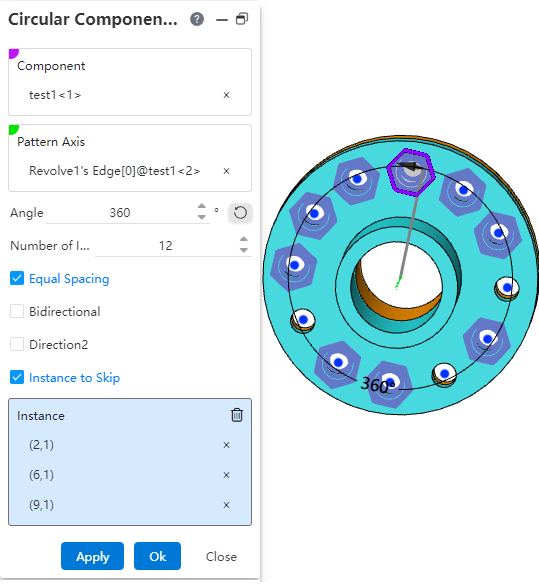
After checking the "Skip Instance" option, pick the origin of the instance to be skipped in the preview model, and the preview effect is as shown in the following figure:
Click "OK" to complete the operation, The effect is shown in the following figure: