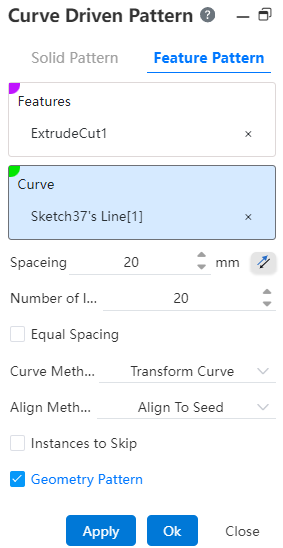
# Curve Driven Pattern
An entity or feature is arranged in a curved shape, and the entity or feature is copied at a set distance for a limited time.
Click the toolbar to open the Curve Array Command dialog box, the command interface is shown in the following figure.
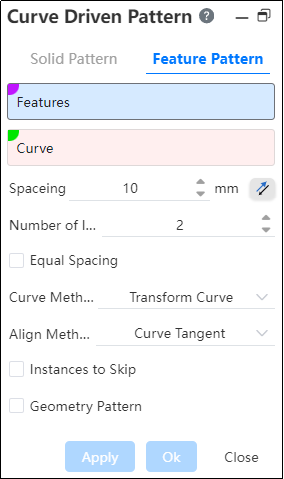
Curve array command is divided into two command pages: Entity Array, Feature Array, corresponding to two different array types.
# Solid Pattern
Entities: Pick up entities that require array operations.
Curve: Pick a curve, sketch line, or solid edge as the array path, you can select multiple options.
Note:
The multi-selection line segment must be a continuous line segment, and the picked curve can be open-loop or closed-loop.
Distance: Sets the spacing of the curve array. When Equal Spacing is checked, the Distance parameter cannot be adjusted.
Number of instances: The number of entities arrayed in the current direction.
Curve method: There are two options, "Convert Curve" and "Isometric Curve".
Note:
- Conversion curve: starting from the position of the source entity, array the instance at a certain distance along the selected curve line, and the source entity is the first array;
- Isometric curve: Starting at the start of the curve, each instance is based on the vertical distance from the source instance to the origin of the selected curve as the reference along the curve array, and the curve starts as the first array.
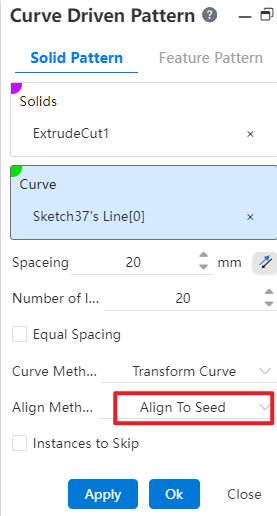
- Alignment method: There are two options, Align with Curve and Align to Source.
Note:
- Tangent to curve: Each instance is arrayed in the direction in which the curve is tangent.
- Align to Source: Each instance of the array is aligned the same way as the source array.
Equal Spacing: Selected by default, the spacing is calculated by averaging the instance count of the total distance of the curve segment, and the distance control parameter cannot be adjusted.
Skip Over Instance: When checked, select the model you want to skip in the array preview and do not generate the model.
Example 1: Create a solid and a curve with the alignment Tangent to Curve, as shown in the following image.
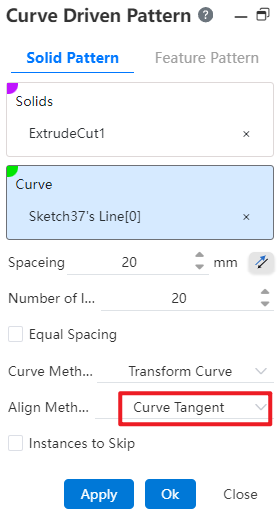
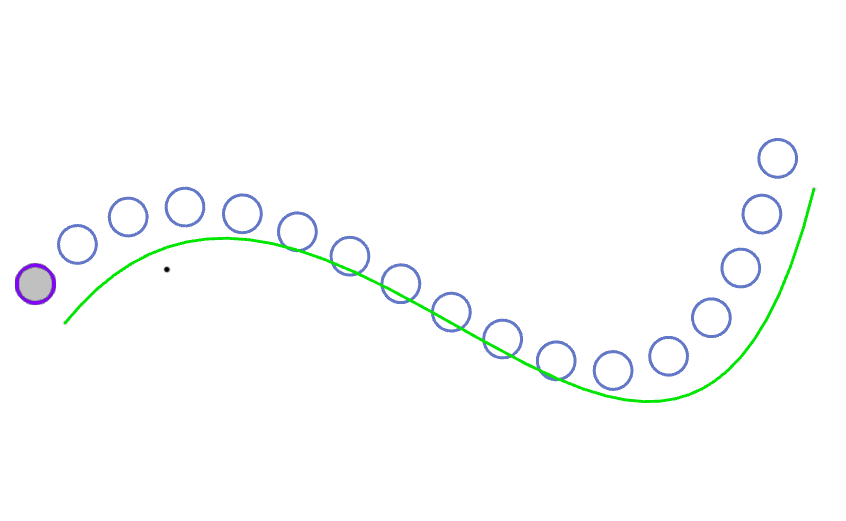
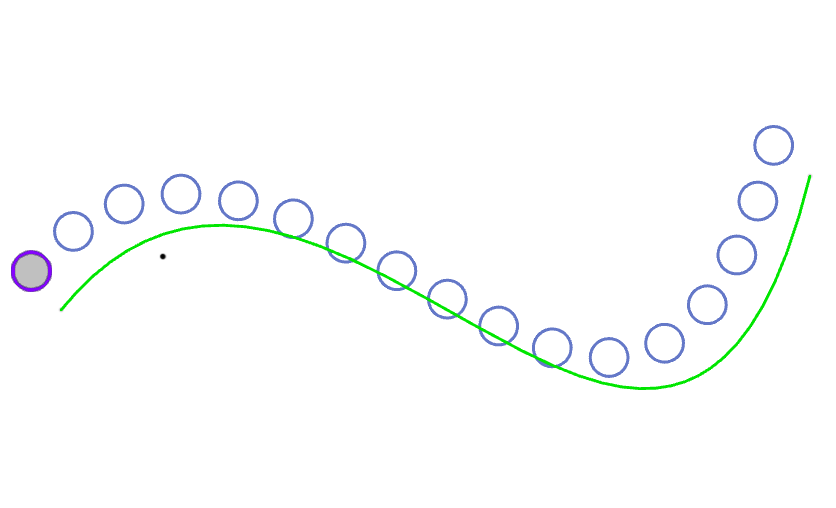
Example 2: Create an entity and a curve with the alignment "Align to Source", as shown in the following image.
# Feature Pattern
- Features: Pick up the features that require an array operation.Support selecting already arrayed features as source features for further arraying.
Note:
Arrays of multiple features can only be made on one entity; Each time a feature is regenerated, it is applied to the same entity, and if the feature is in an entity that does not exist, the pattern fails.
- Curve: Pick a curve, sketch line, or solid edge as the array path, you can select multiple options.
Note:
The multi-selection line segment must be a continuous line segment, and the picked curve can be open-loop or closed-loop.
Distance: Sets the spacing of the curve array. When Equal Spacing is checked, the Distance parameter cannot be adjusted.
Number of instances: The number of features patterned in the current direction.
Equal spacing: When checked by default, the spacing is calculated by averaging the number of instances of the total distance of the curve segment, and the distance control parameter cannot be adjusted.
Curve method: There are two options, "Convert Curve" and "Isometric Curve". Same entity array
Alignment method: There are two options, Align with Curve and Align to Source. Same entity array
Geometry Pattern: Generates a pattern using only the geometry (faces and edges) of the feature, not every instance of the pattern and solves the feature.
Note:
The Geometry Pattern option accelerates feature generation and reconstruction. However, if the faces of some features are merged with the rest of the part, you cannot check a geometry array.
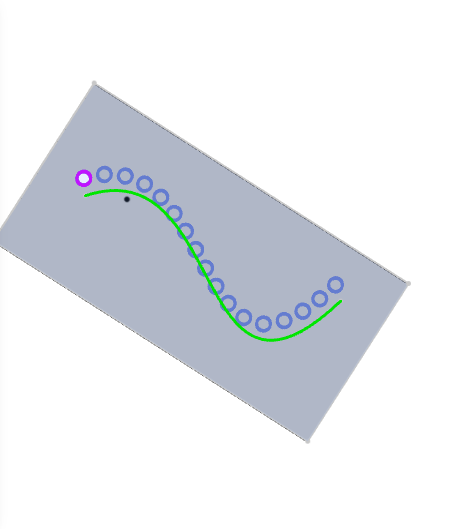
Example: Taking the hole feature as an example, using the curve as the path, the feature array preview effect is shown in the following figure.